Definition
Wave motion
A single frequency traveling wave will take the form of a sine wave. A snapshot of the wave in space at an instant of time can be used to show the relationship of the wave properties frequency, wavelength and propagation velocity.
The motion relationship "distance = velocity x time" is the key to the basic wave relationship. With the wavelength as distance, this relationship becomes = vT. Then using f=1/T gives the standard wave relationship.
The motion relationship "distance = velocity x time" is the key to the basic wave relationship. With the wavelength as distance, this relationship becomes = vT. Then using f=1/T gives the standard wave relationship.
Definition
Wave Number
The wave number is the spatial frequency of a wave, either in cycles per unit distance or radians per unit distance. It can be envisaged as the number of waves that exist over a specified distance (analogous to frequency being the number of cycles or radians per unit time).
Wave number is given as the reciprocal of wavelength.
Wave number is given as the reciprocal of wavelength.
Definition
Frequency of Wave
Wavelength is also measured in metres (m) - it is a length after all. The frequency, f, of a wave is the number of waves passing a point in a certain time. We normally use a time of one second, so this gives frequency the unit hertz (Hz), since one hertz is equal to one wave per second.
Definition
Angular Frequency
Angular frequency (also referred to by the terms angular speed, radial frequency, circular frequency, orbital frequency, radian frequency, and pulsatance) is a scalar measure of rotation rate. It refers to the angular displacement per unit time (e.g., in rotation) or the rate of change of the phase of a sinusoidal waveform (e.g., in oscillations and waves), or as the rate of change of the argument of the sine function.
Angular frequency (or angular speed) is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity. The term angular frequency vector is sometimes used as a synonym for the vector quantity angular velocity.
Angular frequency (or angular speed) is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity. The term angular frequency vector is sometimes used as a synonym for the vector quantity angular velocity.
Definition
Time period of a travelling wave
The period of oscillation T of a wave is defined as the time any string element takes to move through one complete oscillation.
A wave is described by the equation: .Find the time period.For a wave given by ,
A wave is described by the equation: .Find the time period.For a wave given by ,
Formula
General form of equation of wave

General form of equation of wave.
Diagram
Inferring parameters from given wave equation
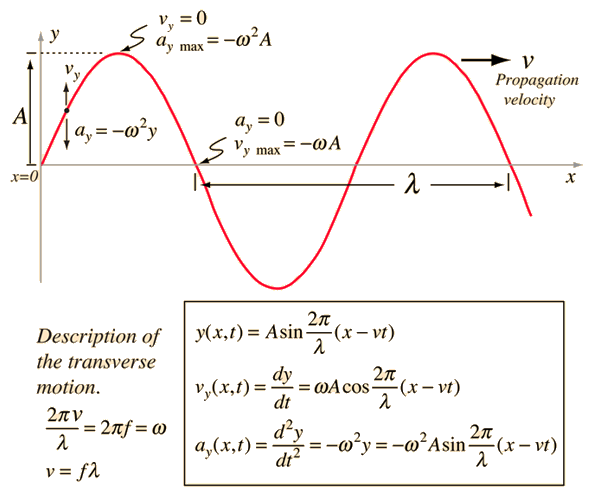
Inferring parameters from given wave equation
General form of equation of wave.
General form of equation of wave.
Definition
Period of a travelling wave

The wave period is the measure of time it takes for the wave cycle to complete. We usually measure the wave period in seconds and represent it with the letter T. Time period is given as the reciprocal of frequency of the wave.
Definition
Classification of Waves
Transverse Waves - Displacement of the medium is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave.To understand this it is good to think of a rope being held still by person B and being moved up and down by person A. The direction of propagation is from person A to B, so you will see the waves move along this way. But the displacement will be up and down.
Definition
Classification of Waves
Longitudnal Waves - Displacement of the medium is parallel to the direction of propagation of the wave.
A good example for this is a slinky being pushed along the table, the propagation will be along the table and so will the displacement of all the 'rings'.
Example
Phase difference between two points in a wave
Example: What is the phase difference between the particle at one compression and another particle in third compression?
Solution:
Phase difference between two successive compression is
phase difference between a particle at one compression and in third compression is
Solution:
Phase difference between two successive compression is
phase difference between a particle at one compression and in third compression is
Formula
Relation between wavelength, wave velocity and frequency
where speed of sound, frequency, wavelength
| BookMarks |
Page 11 Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15
0 Comments
Post a Comment