Definition
Ray diagram for light coming from candle and falling on plane mirror

Definition
Convergent, divergent and parallel beam of light
A convergent beam of light: Light rays comes together (converges) after reflection and refraction at a single point known as the focus.
Divergent beam of light : Light rays from a point source of light travel in all directions, moving away with time. Such a beam of light is called a divergent beam of light.
Parallel beam of light: A parallel beam of light is light that is parallel to each other when coming from the source of light.
Divergent beam of light : Light rays from a point source of light travel in all directions, moving away with time. Such a beam of light is called a divergent beam of light.
Parallel beam of light: A parallel beam of light is light that is parallel to each other when coming from the source of light.
Definition
Reflection
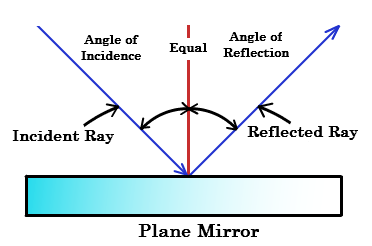
Reflection: When light falls on any object and bounce back to the same medium by changing direction, the phenomena is called reflection of light. Reflection can be regular and irregular reflections.The given figure shows reflection from plane mirror.
Definition
Regular and Irregular Reflection

Regular Reflection: 1. Reflection from a polished surface is called regular reflection.
2. parallel rays remain parallel after reflection.
Irregular Reflection:
1. Reflection from a rough surface is called diffuse reflection.
2. Parallel rays do not remain parallel after reflection.
2. parallel rays remain parallel after reflection.
Irregular Reflection:
1. Reflection from a rough surface is called diffuse reflection.
2. Parallel rays do not remain parallel after reflection.
Definition
Regular and diffused reflection

Regular reflection occurs at the surface of a plane surface like a plane mirror. Reflected rays after regular reflection are parallel.
Diffused reflection occurs at the surface of a rough surface like cardboard. Reflected rays after regular reflection are not parallel.
Note: Laws of reflection are valid in both the cases.
Diffused reflection occurs at the surface of a rough surface like cardboard. Reflected rays after regular reflection are not parallel.
Note: Laws of reflection are valid in both the cases.
Definition
Reflection

Reflection: Bouncing back of a light ray after hitting a surface.
Incident ray: The light ray which strikes the surface.
Reflected ray: The light ray which returns from the surface after reflection.
Normal: An imaginary line perpendicular to the surface passing from the point of contact.
Angle of incidence: Angle between the incident ray and the normal
Angle of reflection : Angle between the reflected ray and the normal.
Incident ray: The light ray which strikes the surface.
Reflected ray: The light ray which returns from the surface after reflection.
Normal: An imaginary line perpendicular to the surface passing from the point of contact.
Angle of incidence: Angle between the incident ray and the normal
Angle of reflection : Angle between the reflected ray and the normal.
Definition
Laws of Reflection

1) Angle made by the incident light with the normal is equal to the angle made by the reflected light with the normal.(As shown in figure)
2) Incident light ray, reflected light ray and normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
3)The reflected ray and the incident ray are on the opposite sides of the normal.
2) Incident light ray, reflected light ray and normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
3)The reflected ray and the incident ray are on the opposite sides of the normal.
Law
Laws of reflection
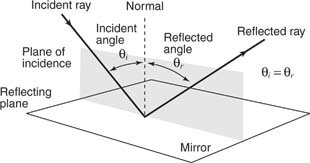
Laws of reflection states that:
- The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
- Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
| BookMarks |
Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15 Page 16 Page 17 Page 18 Page 19 Page 20 Page 21
Page 22 Page 23 Page 24
0 Comments
Post a Comment