Definition
Description of prism

A prism is an object made up of a transparent material like glass or plastic that has at least two flat surfaces that form an acute angle (less than 90 degrees). White light is comprised of all the colors of the rainbow. When white light is passed through a prism, the colors of the rainbow emerge from the prism.
Types of prism
1. Dispersive prisms 2. Reflective prisms 3. Beam-splitting prisms 4. Polarizing prisms 5. Deflecting prisms and many more.
Types of prism
1. Dispersive prisms 2. Reflective prisms 3. Beam-splitting prisms 4. Polarizing prisms 5. Deflecting prisms and many more.
Definition
Terms related to prism

Angle of prism: The angle between the two sides of the reflecting faces of prism is called angle of prism.
Angle of deviation (): Angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray is called the angle of deviation.
Angle of deviation (): Angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray is called the angle of deviation.
Definition
Angle of deviation

Definition:
The angle through which ray of light turns away from its original path on passing through a prism is called angle of deviation.
The angle through which ray of light turns away from its original path on passing through a prism is called angle of deviation.
Definition
Angle of deviation
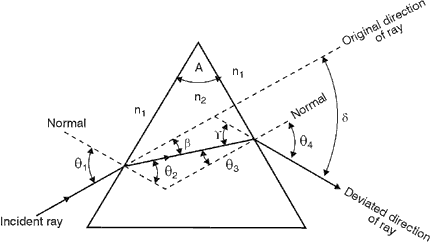
The angle of deviation through a triangular prism is defined as the angle between the incident ray and the emerging ray (angle ). It can be shown that when the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of refraction for the emerging ray, the angle of deviation is at a minimum.
Definition
Prism

A prism is a transparent refracting medium bounded by five plane surfaces inclined at some angles. It bends a light two times and emergent ray is at an angle to the incident ray.
Definition
Angle of deviation

Angle of deviation () is the angle between emergent ray and incident ray.
For a single refracting surface,
For a prism,
where is the angle of the prism.
For angle of minimum deviation, is minimum and
For small ,
For a single refracting surface,
For a prism,
where is the angle of the prism.
For angle of minimum deviation, is minimum and
For small ,
Example
Deviation of light ray due to reflection from a plane surface

Example: Two plane mirrors are inclined to each other with their reflecting faces making acute angle. A light ray is incident on one plane mirror. Find the total deviation after two successive reflections.
Solution:
As indicated in the figure,
If i be the angle of incidence, r be the angle of reflection,
Hence,
Also, using the sum of angles of a triangle,
Thus,
Which means, that the deviation is independent of either the angle of incidence and also the angle of relection. It only depends on the angle between the mirrors.
Solution:
As indicated in the figure,
If i be the angle of incidence, r be the angle of reflection,
Hence,
Also, using the sum of angles of a triangle,
Thus,
Which means, that the deviation is independent of either the angle of incidence and also the angle of relection. It only depends on the angle between the mirrors.
Example
Calculate angle between emerging rays

Example: A beam is incident parallel on the prism shown in the figure. Find the angle between emerging rays. .
Solution:
We have:
Given that
Therefor the ray is refracted out.
Also,
Hence
Solution:
We have:
Given that
Therefor the ray is refracted out.
Also,
Hence
| BookMarks |
Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15 Page 16 Page 17 Page 18 Page 19 Page 20 Page 21
Page 22 Page 23 Page 24
0 Comments
Post a Comment