Definition
Images formed by spherical mirrors for object placed at different distances

When a object is placed far from the concave mirror it will form the real, diminished and inverted image of object on screen as shown in 1st diagram.
When a object is placed near the concave mirror it will form the real,magnified and inverted image of object on screen as shown in 2nd diagram.
When a object is placed near the concave mirror it will form the real,magnified and inverted image of object on screen as shown in 2nd diagram.
Result
Describe the characteristics of the images formed by concave mirror for different object locations.

Result
Describe the characteristics of the images formed by convex mirror for different object locations.

Diagram
Ray diagram of image formation by spherical mirrors

Image shows the ray diagram for various positions of the object for concave and convex mirrors.
Diagram
Image formed by concave and convex mirror
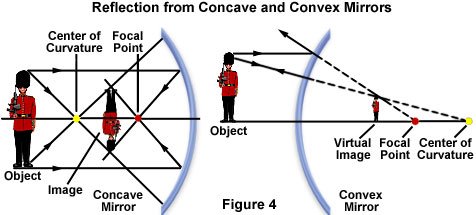
The diagram presented below in figure illustrates the reflection patterns obtained from both concave and convex mirrors. The concave mirror on the left has a reflecting surface that curves inwards that resembles a portion of the interior of a sphere. When light rays that are parallel to the principal, or optical axis, reflect from the surface of a concave mirror, in this case, the rays leading from the soldier's hat and feet, they converge on the focal point in front of the mirror. The distance from the reflecting surface to the focal point is termed the mirror's focal length. The size of the image depends upon the distance of the object from the mirror and it's position with respect to the mirror's surface. In this case, the soldier is placed at the center of curvature and the reflected image is upside down and in front of the mirror's center of curvature.
The convex mirror on the right-hand side of figure, however, has a reflecting surface that curves outward, which resembles a portion of the exterior of a sphere. Light rays parallel to the optical or principal axis are reflected from the surface in a manner that diverges from a focal point that is behind the mirror. Images formed with convex mirrors are always right side up and reduced in size. These images are also termed virtual images because when they occur reflected rays appear to diverge from a focal point behind the mirror.
The convex mirror on the right-hand side of figure, however, has a reflecting surface that curves outward, which resembles a portion of the exterior of a sphere. Light rays parallel to the optical or principal axis are reflected from the surface in a manner that diverges from a focal point that is behind the mirror. Images formed with convex mirrors are always right side up and reduced in size. These images are also termed virtual images because when they occur reflected rays appear to diverge from a focal point behind the mirror.
Diagram
Image formation by spherical mirrors
| Concave mirror | Object position | Image position | Image size | Image nature |
| 1 | Infinity | Focus | Point-sized | Real, inverted |
| 2 | Beyond C | Between C and F | Diminished | Real, inverted |
| 3 | At C | At C | Same size | Real, inverted |
| 4 | Between C and F | Beyond C | Magnified | Real, inverted |
| 5 | At F | infinity | Highly magnified | Real, inverted |
| 6 | Between F and P | Behind the mirror | Magnified | Virtual, erect |
Formula
Mirror formula
Mirror formula is an expression relating the image distance (), object distance () and the focal length ().
Note:
Note:
- Utmost care should be taken regarding sign convention while using mirror formula.
- Focal length of convex mirror is taken as positive and concave mirror as negative.
Diagram
Plot of object distance vs image distance for spherical mirrors

as for mirror formula
and f is constant.
The relation between and is a linear relation, and
For a convex lensThe above equation looks like a hyperbola. Hence correct answer is A as negative u gives positive v.
| BookMarks |
Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15 Page 16 Page 17 Page 18 Page 19 Page 20 Page 21
Page 22 Page 23 Page 24
0 Comments
Post a Comment