Definition
Relative motion of a body
A body is in a state of motion w.r.t. a moving body if its position changes with time as seen by the moving body, else it is at a state of rest w.r.t the moving body. This occurs if and only if the velocity of the two bodies are equal at all instances of time. For example, two people standing on the surface of the earth see each other to be at rest. Actually, they are both moving as the earth is rotating.
Example
Triangle Law of Vector addition in Relative Motion

A swimmer can swim in still water with speed and the river flowing with velocity . To cross the river in shortest distance, he should swim making an angle with the upstream. Find ratio of the time taken to swim across in the shortest time to that in swimming across over shortest distance.
For shortest distance , Time taken
For shortest time , Time taken
Ratio of times taken for shortest time to that of shortest path
For shortest distance , Time taken
For shortest time , Time taken
Ratio of times taken for shortest time to that of shortest path
Definition
Relative Acceleration
The relative acceleration (also or ) is the acceleration of an object or observer B in the rest frame of another object or observer A.
Acceleration of B relative to A is
Acceleration of B relative to A is
Definition
Relative Velocity
The relative velocity (also or ) is the velocity of an object or observer B in the rest frame of another object or observer A.
Velocity of B relative to A is =
Velocity of B relative to A is =
Example
Interpreting Relative Motion Through Graphs
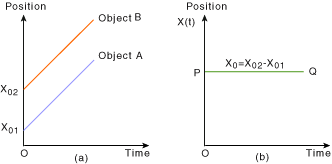
Relative position between the particles is not changing over the passage of time therefore relative position has become constant.
Example
Problems on relative motion between point objects
Bodies are dropped from a height in successive intervals of half a second. The relative velocity of one with respect to the other is:
At any tme,
(Relative velocity)
At any tme,
(Relative velocity)
Definition
Relative Motion between finite length objects
Example: A car is moving with velocity m/s find its velocity relative to a bike moving with m/s.
Solution:
Relative velocity of car with respect to bike:
Solution:
Relative velocity of car with respect to bike:
Example
Relative motion between point objects moving in two dimensions
Let the velocity of one object is:
Velocity of the other object is:
Relative velocity =
Velocity of the other object is:
Relative velocity =
Example
Objects moving upstream or downstream in a river
A boat takes to travel and back in a still water lake. With water velocity of , the time taken for going upstream of and coming back is given by:
Speed of boat relative to water
Speed downstream
Speed upstream
Time taken with water flow
Speed of boat relative to water
Speed downstream
Speed upstream
Time taken with water flow
Example
Problems on objects crossing a river
A man who can swim at a speed relative to the water wants to cross a river of width , flowing with a speed . The point opposite him across the river is A.
For reaching A, he must have a velocity component along the flow of river. Hence, in the frame of river he must have a component along the river to have zero component in ground frame and hence perpendicular to the flow, he has velocity relative to both frames, Hence, the time taken .
For reaching A, he must have a velocity component along the flow of river. Hence, in the frame of river he must have a component along the river to have zero component in ground frame and hence perpendicular to the flow, he has velocity relative to both frames, Hence, the time taken .
| BookMarks |
Page 11 Page 12 Page 13 Page 14
0 Comments
Post a Comment