Definition
Instantaneous velocity
Instantaneous velocity is defined as the rate of change of displacement with time,where the period of time is narrowed such that it reaches zero.
Note:
1. Direction of instantaneous velocity at any time gives the direction of motion of particle at that point of time.
2. Magnitude of instantaneous velocity equals the instantaneous speed. This happens because for an infinitesimally small time interval, motion of a particle can be approximated to be uniform.
Note:
1. Direction of instantaneous velocity at any time gives the direction of motion of particle at that point of time.
2. Magnitude of instantaneous velocity equals the instantaneous speed. This happens because for an infinitesimally small time interval, motion of a particle can be approximated to be uniform.
Example
Average Velocity
For a body moving with uniform acceleration , initial and final velocities in a time interval are and respectively.
Then, its average velocity in the time interval will be given by:
Average velocity
Substitute, in the above expression,
We get average velocity
Then, its average velocity in the time interval will be given by:
Average velocity
Substitute, in the above expression,
We get average velocity
Definition
Uniform acceleration
A body under constant acceleration is called as uniformly accelerated motion. This happens when a constant external force is applied on the body.
Note:
Direction of acceleration plays a role in the change of velocity. However, direction of acceleration of a body may not be same as the direction of its motion.
Note:
Direction of acceleration plays a role in the change of velocity. However, direction of acceleration of a body may not be same as the direction of its motion.
Definition
Define and calculate instantaneous acceleration
When the object is moving with variable acceleration, then the object possesses different acceleration at different instant. The acceleration of the object at different instant of time or at given time of motion, is called instantaneous acceleration.
Definition
Average Acceleration

Average acceleration is the change in velocity divided by an elapsed time. For instance, if the velocity of a marble increases from 0 to 60 cm/s in 3 seconds, its average acceleration would be 20 cm/s. This means that the marble's velocity will increase by 20 cm/s every second.
Formula
Understand Acceleration as Second Derivative of Displacement
Where is a displacement vector.
Definition
Acceleration as a rate of change of velocity with respect to displacement
Acceleration is defined as
Example:
If the velocity of a particle is given by , then find its acceleration.
Solution:
Differentiate both sides w.r.t , we get:
Formula
Definition of Jerk
Rate of change of acceleration is defined as jerk.
jerk =
jerk =
Result
Distance in nth second(distance-time graph)
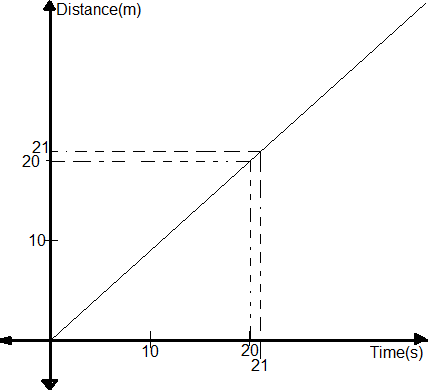
Distance traveled in nth second can be found using distance time-graph. In the given figure, distance after is and after is . Hence, distance traveled in sec is .
Definition
Average velocity from a displacement-time graph

Average velocity equals the ratio of net displacement and the time taken.
Example:
In the given plot, for ,
Displacement
Hence, average velocity is given by
Example:
In the given plot, for ,
Displacement
Hence, average velocity is given by
| BookMarks |
Page 11 Page 12 Page 13 Page 14
0 Comments
Post a Comment