Result
Primary cells v/s secondary cells
| S.No | Primary cell | Secondary Cell |
| 1 | Chemical reaction is irreversible. | Chemical reaction is reversible. |
| 2 | Chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. | Chemical energy is converted into electrical energy during energy supply & electrical energy is converted into chemical energy during charging. |
| 3 | Cannot be recharged | Can be recharged |
| 4 | Internal resistance is high. | Internal resistance is low. |
| 5 | Can supply weak currents only. | Can supply weak and high currents. |
| 6 | Light and cheap. | Heavy and costly. |
| 7 | Example: Simple voltaic cell, Dry cell | Example: Lead (or acid) accumulator, Ni-Fe |
Definition
Methods of Removing Polarization
1. Mechanical Method - In this method, copper rod is taken out and cleaned with a brush, time to time. Although hydrogen layer gets removed, yet this method is not of practical use and is seldom used.
2. Chemical Method - In this method, hydrogen deposited on copper rod is converted into water bubbles by an oxidizing agent such as manganese dioxide, nitric acid, potassium dichromate etc.
3. Electrochemical Method - Here the positive plate is kept ina particular direction solution, which changes hydrogen ions into different positive ions. Thus, the polarization is removed. For example Copper sulphate solution si used in daniel cell.
2. Chemical Method - In this method, hydrogen deposited on copper rod is converted into water bubbles by an oxidizing agent such as manganese dioxide, nitric acid, potassium dichromate etc.
3. Electrochemical Method - Here the positive plate is kept ina particular direction solution, which changes hydrogen ions into different positive ions. Thus, the polarization is removed. For example Copper sulphate solution si used in daniel cell.
Example
Primary cells

A primary cell is a battery that is designed to be used once and is discarded, and not recharged with electricity and reused like a secondary cell.
The electrochemical reaction occurring in the cell is not reversible, rendering the cell unrechargeable. As a primary cell is used, chemical reactions in the battery use up the chemicals that generate the power; when they are gone, the battery stops producing electricity and is useless.
The electrochemical reaction occurring in the cell is not reversible, rendering the cell unrechargeable. As a primary cell is used, chemical reactions in the battery use up the chemicals that generate the power; when they are gone, the battery stops producing electricity and is useless.
Definition
Secondary Cell
" In this cell the electrical energy is stored in the form of chemical energy and then the chemical energy is again transformed into electrical energy".
Definition
Electro-motive force
The potential difference between the terminal of a cell when no current is drawn from it is called electromotive force (). Its unit is volt (V).
Result
Factors affecting e.m.f.
E.m.f. of a cell depends upon the material of electrodes and electrolyte used in the cell. It is independent of shape of electrodes, distance between electrodes and the amount of electrolyte.
Result
Factors affecting internal resistance
The internal resistance of a cell depends on:
- Surface area of electrodes (more surface area less resistance)
- Distance between the electrodes (more distance more resistance)
- Nature and concentration of electrolyte (higher concentration more resistance)
- Temperature of electrolyte (more temperature more resistance)
Definition
Terminal voltage
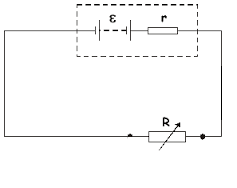
The potential difference between the electrodes of the cell when current is drawn from it is called the terminal voltage of the cell. It is smaller than the e.m.f. of the cell because of the internal resistance of the cell. When current flows, some energy is spent in overcoming the internal resistance (r) of the cell.
Definition
Voltage drop in a cell
When current is drawn through a circuit, the voltage supplied by the battery is not equal to the emf but actually decreases. This decrease in potential across the ends of the battery is known as voltage drop. Voltage drops is undesired in circuit elements like conductors,contacts,connectors and internal resistances of the source as the supplied energy is lost but it is desired in loads and across other active circuit elements as the energy given is converted into work.
Formula
Relationship between emf and terminal voltage
emf = Terminal Voltage + Internal drop in the cell
where = internal resistance.
where = internal resistance.
| BookMarks |
Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15 Page 16
0 Comments
Post a Comment