Example
Resistors in series and parallel
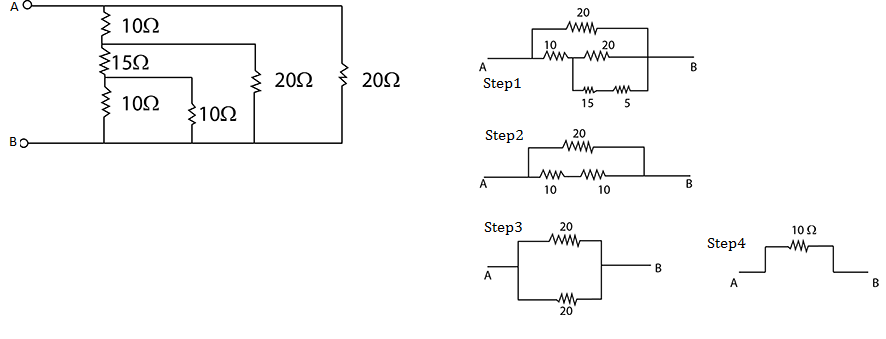
The effective resistance between A and B is:The circuit can be reduced as shown in the figure to obtain the equivalent resistance.
In step 1 The innermost rectangle has two resistances in parallel. 5 equivalent resistance is kept in place of both.
Step 2. In step one 15 and 5 are in series which combined are in parallel to 20 . The equivalent resistance of 10 is kept in the place of them.
Step 3. In step 2 now two 10 are in series. The equivalent resistance of is kept.
Step 4. In step 3 two resistance are in parallel, which give equivalent resistance between A and B as .
In step 1 The innermost rectangle has two resistances in parallel. 5 equivalent resistance is kept in place of both.
Step 2. In step one 15 and 5 are in series which combined are in parallel to 20 . The equivalent resistance of 10 is kept in the place of them.
Step 3. In step 2 now two 10 are in series. The equivalent resistance of is kept.
Step 4. In step 3 two resistance are in parallel, which give equivalent resistance between A and B as .
Example
Multiple resistors in series and parallel

In the circuit given below all resistances are of values ohm each. The currents and given that the e.m.f. of the cell is are:
Example
Electrical resistance circuits using symmetry

Twelve resistances, each of resistance are connected in the circuit as shown in the figure. Net resistance between points and would be:By symmetric rule, and can be removed.
[ no current flows through them]
Then the circuit becomes as shown.
[ no current flows through them]
Then the circuit becomes as shown.
Shortcut
Procedure to solve Infinite circuits

Let the infinite circuit be as shown in figure (a). Here are the steps to solve it.
- Assume the equivalent resistance of the system in the dotted box be .
- Then calculate the equivalent resistance of the whole system taking in parallel with the remaining system as shown in figure (b).
- Now this final calculated value is also ( the part of infinity is also infinity).
Example
Electrical resistance using star-delta rule

The resistance of all the wires between any two adjacent dots is . The equivalent resistance between and as shown in Figure is:
Here the equivalent resistance of each triangle is
Now reduce the side by connecting resistance in series as shown in figure.
here, .
Now the circuit is a balanced Wheatstone bridge . So middle resistor R is not working.
Thus,
Here the equivalent resistance of each triangle is
Now reduce the side by connecting resistance in series as shown in figure.
here, .
Now the circuit is a balanced Wheatstone bridge . So middle resistor R is not working.
Thus,
Diagram
Positive and negative terminals of an electric cell

Every cell has a positive and a negative terminal and based on their polarity it is connected in the electrical circuit.
For example in a circuit positive terminal of a cell is always connected to a negative terminal of the other cell, otherwise the current will not flow in the circuit as the polarity become same on both the side and no potential difference will be there.
For example in a circuit positive terminal of a cell is always connected to a negative terminal of the other cell, otherwise the current will not flow in the circuit as the polarity become same on both the side and no potential difference will be there.
| BookMarks |
Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15 Page 16
0 Comments
Post a Comment