Definition
Internal resistance using potentiometer
We can also use a potentiometer to measure internal resistance of a cell. For this the cell (emf ) whose internal resistance () is to be determined is connected across a resistance box through a key . With key open, balance is obtained at length . Then,
When key is closed, the cell sends a current () through the resistance box (). If is the terminal potential difference of the cell and balance is obtained at length ,
so,
which is the internal resistance of the given cell.
When key is closed, the cell sends a current () through the resistance box (). If is the terminal potential difference of the cell and balance is obtained at length ,
so,
which is the internal resistance of the given cell.
Definition
Precautions while using a potentiometer
1. Jockey should not be dragged along the wire.2. The current value should be as small as possible.3. Current should be passed only while taking the readings.
Definition
Potentiometer vs voltmeter
| Voltmeter | Potentiometer |
| A voltmeter cannot be used to measure the emf of a cell because a voltmeter draws some current from the cell. | To measure a cell's emf a potentiometer is used since in a potentiometer measurement no current is flowing. |
| Measures emf of cell approximately | Measures emf of cell very accurately |
| Sensitivity is low | Sensitivity is high |
Definition
Relation between resistance and temperature
where is the initial resistance and is the coefficient of thermal expansion. Change in temperature brings about a change in the resistance .
Definition
Dynamic resistance
Dynamic resistance is used to quantify the resistance of non-ohmic materials. It is defined as the ratio of differential change in voltage to a differential change in current.
Note:
Dynamic resistance is itself a function of the current (or voltage) through the material for a non-ohmic conductor.
Note:
Dynamic resistance is itself a function of the current (or voltage) through the material for a non-ohmic conductor.
Definition
Rheostat as a current controller
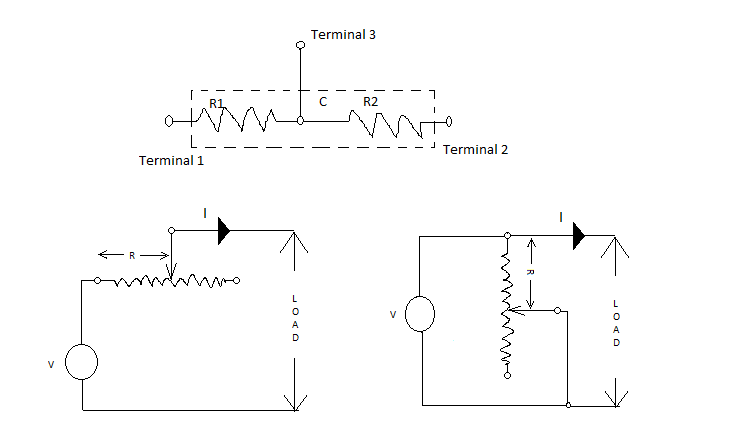
The electrical component rheostat, have 3 terminals. Two terminals are the begining and end of the wire( and ), while the 3rd terminal is the movable contact which can be moved along the length of the wire().Now by using two terminals(One of them ), Rheostat functions as a current limiter. The value of current flow depends on the resistance in its path, so by adjusting the contact the value of resistance exhibited can be altered thus the current flow can be controlled.
This can accomplished in two ways:In Shunt or in Series.
This can accomplished in two ways:In Shunt or in Series.
Definition
Rheostat as a potential divider

A rheostat is a resistance element with considerable length. It is usually metallic in nature. The defining equation is
Where;
resistivity of the element.
length of the wire.
area of cross section of the wire.
The electrical component rheostat, have 3 terminals,two terminals are the begining and end of the wire ( and ), while the 3rd terminal is the movable contact which can be moved along the length of the wire(). and remains the same throughout; thus the resistance between terminals is decided by the length of wire between them.
The length to is while to is . This results in two resistances and ; causing an equivalent circuit.By adding a voltage source across and ; desired voltage can be obtained across and ground by tuning the point of contact C on the rheostat.
Where;
resistivity of the element.
length of the wire.
area of cross section of the wire.
The electrical component rheostat, have 3 terminals,two terminals are the begining and end of the wire ( and ), while the 3rd terminal is the movable contact which can be moved along the length of the wire(). and remains the same throughout; thus the resistance between terminals is decided by the length of wire between them.
The length to is while to is . This results in two resistances and ; causing an equivalent circuit.By adding a voltage source across and ; desired voltage can be obtained across and ground by tuning the point of contact C on the rheostat.
Definition
Meter bridge

A meter bridge consists of a wire of length and of uniform cross-sectional area stretched taut and clamped between two thick metallic strips bent at right angles with two gaps across which resistors are to be connected. The end points where the wire is clamped are connected to a cell through a key. One end of a galvanometer is connected to the metallic strip midway between the two gaps. The other end of the galvanometer is connected to a jockey which moves along the wire to make electrical connection. is an unknown resistance connected across one of the gaps. Across the other gap, we connect a standard known resistance . The jockey is connected to some point D on the wire, a distance cm from the end A.The portion AD of the wire has a resistance , where is the resistance of the wire per unit centimeter. The portion DC of the wire similarly has a resistance .
The meter bridge works on the principle of Wheatstone bridge. At balance condition:
The meter bridge works on the principle of Wheatstone bridge. At balance condition:
| BookMarks |
Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15 Page 16
0 Comments
Post a Comment