Example
Problems on total equilibrium involving friction where line of action of normal force changes

Example: A cubical block of mass and side rests on a rough horizontal surface with coefficient of friction . A horizontal force
is applied on the block as shown in the figure. If the coefficient of friction is sufficiently high so that the block does not slide before toppling, what is the minimum force required to topple the block?
Solution:
Considering case 1, when minimum force is applied,
Now,
when the force exceeds some value, block topples
Taking moment about the toppling axis,
................ Still in equilibrium
is applied on the block as shown in the figure. If the coefficient of friction is sufficiently high so that the block does not slide before toppling, what is the minimum force required to topple the block?
Solution:
Considering case 1, when minimum force is applied,
Now,
when the force exceeds some value, block topples
Taking moment about the toppling axis,
................ Still in equilibrium
Definition
Pure Rotational motion

A body has pure rotational motion when one point of the body is fixed and all the other points of the body rotate around it. The body is rotating about an axis that passes through the fixed point and is normal to the plane of motion. In this case, all the points of the body have circular motion.
Definition
Rotation plus Translation motion
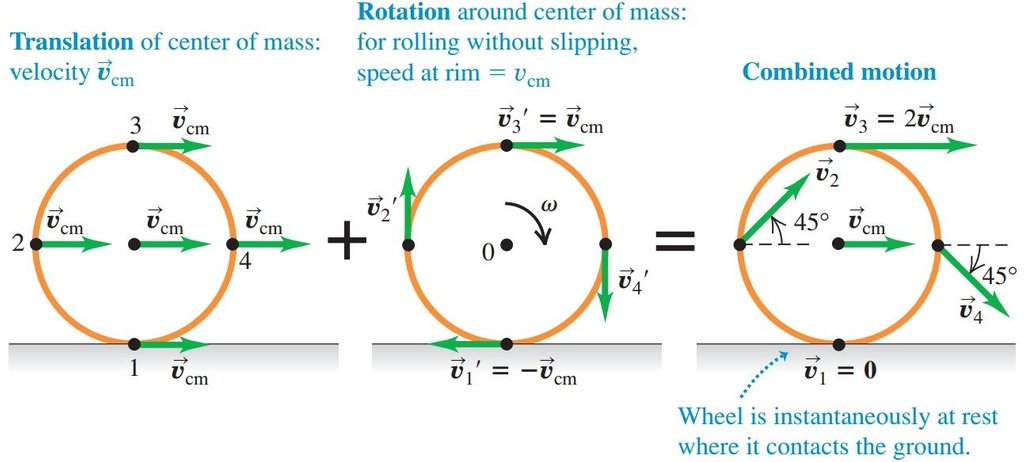
Rolling motion:
An important case of combined translation and rotation is rolling without slipping, when a body like a sphere, the wheel rolls on a surface, the motion can be treated as the combination of both translational motions of the centre of mass and rotational motion about an axis passing through the centre of mass.
An important case of combined translation and rotation is rolling without slipping, when a body like a sphere, the wheel rolls on a surface, the motion can be treated as the combination of both translational motions of the centre of mass and rotational motion about an axis passing through the centre of mass.
Example
Examples of Rolling motion
1. Ball rolling down a hill.
2. Rolling of Bike wheels.
3. Motion of Bowling ball.
4. Motion of snooker ball on table.
2. Rolling of Bike wheels.
3. Motion of Bowling ball.
4. Motion of snooker ball on table.
Definition
Pure Transnational motion

The velocity of all particles of the body will be same as that of the velocity of the centre of mass of a body is known as translational motion of the body.
In the figure it can be seen that velocity of particles 1,2,3,4,... of a body is same as that of the centre of mass, hence its in pure translational motion.
In the figure it can be seen that velocity of particles 1,2,3,4,... of a body is same as that of the centre of mass, hence its in pure translational motion.
Definition
Precession

Definition:
The motion of the rotation axis of a rigid body, as a spinning top, when a disturbing torque is applied while the body is rotating such that the rotation axis describes a cone, with the vertical through the vertex of the body as the axis of the cone, and the motion of the rotating body is perpendicular to the direction of the torque.
Example:
The Precession of the Earth's Axis-
The Earth's axis rotate just as a spinning top does. The period of precession is about 26,000 years.
Therefore, the North Celestial Pole will not always be pointing towards the same starfield.
Precession is caused by the gravitational pull of the Sun and the Moon on the Earth.
The motion of the rotation axis of a rigid body, as a spinning top, when a disturbing torque is applied while the body is rotating such that the rotation axis describes a cone, with the vertical through the vertex of the body as the axis of the cone, and the motion of the rotating body is perpendicular to the direction of the torque.
Example:
The Precession of the Earth's Axis-
The Earth's axis rotate just as a spinning top does. The period of precession is about 26,000 years.
Therefore, the North Celestial Pole will not always be pointing towards the same starfield.
Precession is caused by the gravitational pull of the Sun and the Moon on the Earth.
Example
Angular Velocity of a rigid body
Example: A circular disc is rotating with angular velocity . A man
standing at the edge walks towards the centre of disc then how it will affect the angular velocity ?
Solution:
Net external torque is zero)
will increase (as moment of inertia decreases.)
standing at the edge walks towards the centre of disc then how it will affect the angular velocity ?
Solution:
Net external torque is zero)
will increase (as moment of inertia decreases.)
Example
Torque about an axis for a point object
Torque about an axis is given by:
The torque for a point object at a perpendicular distance from the line of application of force is given by:
Torque =
The torque for a point object at a perpendicular distance from the line of application of force is given by:
Torque =
| BookMarks |
Page 11 Page 12
0 Comments
Post a Comment