Definition
Properties of nuclear force
- The nuclear force is much stronger than the Coulomb force acting between charges or the gravitational forces between masses. The nuclear binding force has to dominate over the Coulomb repulsive force between protons inside the nucleus. This happens only because the nuclear force is much stronger than the coulomb force. The gravitational force is much weaker than even Coulomb force.
- The nuclear force between two nucleons falls rapidly to zero as their distance is more than a few femtometres. This leads to saturation of forces in a medium or a large-sized nucleus, which is the reason for the constancy of the binding energy per nucleon.
- The nuclear force between neutron-neutron, proton-neutron and proton-proton is approximately the same. The nuclear force does not depend on the electric charge.
Definition
Potential energy variation as a function of their separation

Definition
Explain Cosmic ray showers

An air shower is an extensive (many kilometres wide) cascade of ionized particles and electromagnetic radiation produced in the atmosphere when a primary cosmic ray (i.e. one of extraterrestrial origin) enters the atmosphere. The term cascade means that the incident particle, which could be a proton, a nucleus, an electron, a photon, or (rarely) a positron, strikes an atom's nucleus in the air so as to produce many energetic hadrons. The unstable hadrons decay in the air speedily into other particles and electromagnetic radiation, which are part of the shower components.
Definition
Explain construction of Bainbridge mass spectrometer to determine mass of nuclei
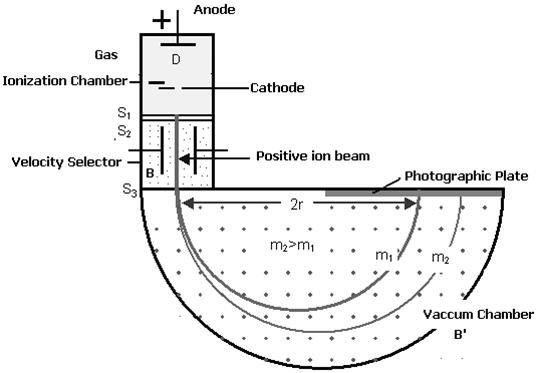
Construction:
(i) Ionization Chamber: Ionization chamber is used to ionize the gas whose mass or isotope is to be determined and positive ions are produced.
(ii) Velocity Selector: Velocity selector has two fields electric and magnetic field both are applied perpendicular to the moving ion beam. A potential (V) is applied between two electrodes to produce the electric field. A magnetic field (strength B) is applied at right angles to the electrostatic field and so the electrostatic and electromagnetic forces act in opposite directions to each other.
(iii) Vacuum / Analyzing Chamber: Vacuum / Analyzing Chamber is a semi-spherical cavity in which another magnetic field 'B is applied perpendicular to the moving positive ion.
(i) Ionization Chamber: Ionization chamber is used to ionize the gas whose mass or isotope is to be determined and positive ions are produced.
(ii) Velocity Selector: Velocity selector has two fields electric and magnetic field both are applied perpendicular to the moving ion beam. A potential (V) is applied between two electrodes to produce the electric field. A magnetic field (strength B) is applied at right angles to the electrostatic field and so the electrostatic and electromagnetic forces act in opposite directions to each other.
(iii) Vacuum / Analyzing Chamber: Vacuum / Analyzing Chamber is a semi-spherical cavity in which another magnetic field 'B is applied perpendicular to the moving positive ion.
Definition
Describe baryons

A baryon is a composite subatomic particle made up of three quarks (a triquark, as distinct from mesons, which are composed of one quark and one antiquark). Baryons and mesons belong to the hadron family of particles, which are the quark-based particles.
Definition
Alpha,beta and gamma particles
| Alpha particle | Beta particle | Gamma particle |
| It is a helium atom and contains two neutrons and two protons | It is an electron or a positron emitted by the decay of nucleus | It is an energetic photon or light wave. |
| Heavier than beta and gamma particles | Much lighter than alpha particles | It is a wave unlike alpha and beta particles. |
| Least penetrating energy. A sheet of paper or a 3-cm layer of air is sufficient to stop them. | They can be stopped, for instance, by an aluminium sheet a few millimetres thick or by 3 metres of air. | Highest penetrating energy.Gamma waves can be stopped by a thick or dense enough layer material, with high atomic number materials such as lead or depleted uranium being the most effective form of shielding. |
Definition
The properties of alpha particles
1. The speed of alpha particles is of the order of m/s.
2. Alpha particles strongly ionises the gas through which it passes.
3. Alpha particles rapidly loses its energy as it moves through a medium and therefore its penetrating power is quite small.
4. Alpha particles are positively charged.
5. Alpha particles affect a photographic plate.
6. Alpha particles cause fluorescence on striking a fluorescent material.
2. Alpha particles strongly ionises the gas through which it passes.
3. Alpha particles rapidly loses its energy as it moves through a medium and therefore its penetrating power is quite small.
4. Alpha particles are positively charged.
5. Alpha particles affect a photographic plate.
6. Alpha particles cause fluorescence on striking a fluorescent material.
Definition
Impact parameter

The trajectory traced by an -particle depends on the impact parameter, of collision. The impact parameter is the perpendicular distance of the initial velocity vector of the -particle from the centre of the nucleus.
where is the impact parameter and is the scattering angle.
where is the impact parameter and is the scattering angle.
| BookMarks |
Page 12 Page 13 Page 14
0 Comments
Post a Comment