Definition
Scalar Quantities
A scalar quantity is a quantity which is defined by only magnitude. Some examples of scalar quantities are Mass, Charge, Pressure, etc.
Definition
Vector quantities
Vector quantities are those which have both magnitude and direction and obey vector laws of addition. Some examples of vectors are displacement, velocity, force, etc.
A quantity is called a vector only if it follows all the above three conditions. For example, current is not a vector despite having both magnitude and direction because it does not follow vector laws of addition.
A quantity is called a vector only if it follows all the above three conditions. For example, current is not a vector despite having both magnitude and direction because it does not follow vector laws of addition.
Definition
Scalar
Scalar Quantities:
1. A physical quantity which is having magnitude only but not direction those are scalar quantities.
2. These are one-dimensional quantities.
3. It follows ordinary rules of algebra.
4. The scalar can be divided by any other scalar quantity.
5. It changes due to change in their magnitude only.
6. e.g. mass, work etc
1. A physical quantity which is having magnitude only but not direction those are scalar quantities.
2. These are one-dimensional quantities.
3. It follows ordinary rules of algebra.
4. The scalar can be divided by any other scalar quantity.
5. It changes due to change in their magnitude only.
6. e.g. mass, work etc
Definition
vector
Vector Quantity:
1. A vector quantity is one, that has both magnitude and direction.
2. Are multi-dimensional quantities.
3. It changes with the change in their direction or magnitude or both.
4. Follow rules of vector algebra.
5. Two vectors can never divide.
1. A vector quantity is one, that has both magnitude and direction.
2. Are multi-dimensional quantities.
3. It changes with the change in their direction or magnitude or both.
4. Follow rules of vector algebra.
5. Two vectors can never divide.
Diagram
Direction of vector
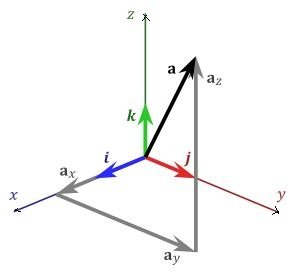
Vector shown in diagram can be represented as
Magnitude of vector a
a =
- component of vector along x-axis
- component of vector along y-axis
- component of vector along z- axis
- unit vectors along x,y and z direction.
Magnitude of vector a
a =
- component of vector along x-axis
- component of vector along y-axis
- component of vector along z- axis
- unit vectors along x,y and z direction.
Result
Scalars and Vectors
Following are some differences listed between scalars and vectors.
| S.No. | Scalars | Vectors |
| 1. | Have only magnitude | Have both magnitude and direction |
| 2. | Algebra: Same as real numbers | Algebra: Follow vector laws of addition |
| 3. | Examples: Mass, charge, etc | Examples: velocity, force, electric field. etc. |
Definition
Free and fixed vectors
Free vector:
A free vector is a vector whose action is not confined to or associated with a unique line in space. Examples: velocity vector, electric field vector, etc.
Sliding vector:
A vector that can be applied at any point on a body as long as it is along its original line of action and doesn't change its effect in the body as a whole. Example: force vector, etc.
Fixed vector:
Fixed vector is that vector whose initial point or tail is fixed. Example: position vector, etc.
A free vector is a vector whose action is not confined to or associated with a unique line in space. Examples: velocity vector, electric field vector, etc.
Sliding vector:
A vector that can be applied at any point on a body as long as it is along its original line of action and doesn't change its effect in the body as a whole. Example: force vector, etc.
Fixed vector:
Fixed vector is that vector whose initial point or tail is fixed. Example: position vector, etc.
Definition
Difference between scalar and vector
| SCALAR QUANTITY | VECTOR QUANTITY | |
| Meaning | Any physical quantity that does not include direction is known as scalar quantity. | Vector quantity is one, that has both magnitude and direction. |
| Quantities | One-dimensional quantities | Multi-dimensional quantities |
| Change | It changes with the change in their magnitude. | It changes with the change in their direction or magnitude or both. |
| Operations | Follow ordinary rules of algebra. | Follow rules of vector algebra. |
| Comparison of two quantities | Simple | Complex |
| Division | Scalar can divide another scalar. | Two vectors can never divide. |
Definition
Axial Vector
Axial vector is a vector which does not change its sign on changing the coordinate system to a new system by a reflection in the origin.
An example of an axial vector is the vector product of two polar vectors, such as A = x m, where A is the angular momentum of a particle, x is its position vector, and m is its momentum vector.
An example of an axial vector is the vector product of two polar vectors, such as A = x m, where A is the angular momentum of a particle, x is its position vector, and m is its momentum vector.
Definition
Equality of vectors
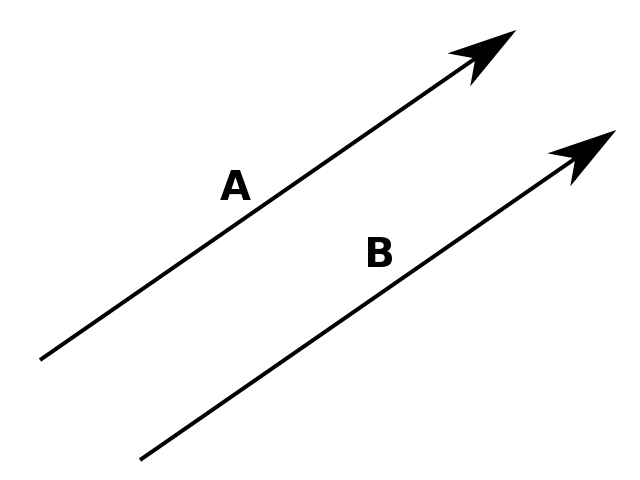
Two vectors are said to be equal if
(i) they have the same magnitude and
(ii) are in the same direction.
If we shift B parallel to A then it will completely superimpose A i.e it has same length and are in the same direction as A, so .
(i) they have the same magnitude and
(ii) are in the same direction.
If we shift B parallel to A then it will completely superimpose A i.e it has same length and are in the same direction as A, so .
| BookMarks |
0 Comments
Post a Comment