Example
Constrained Motion

In a system of elements, free motion is restricted due to some constraints and any relative motion which arises due to these constraints is called constrained motion.
There are 3 types of constrained motion:
There are 3 types of constrained motion:
- Completely constrained motion
- Incompletely constrained motion
- Successfully constrained motion
Example
Spring two mass system

Assume a spring of spring constant , one end is attached to a block of mass and other end is attached to block of mass , they are placed on a smooth horizontal surface. and are moving with velocity and in the same direction respectively. ()
After a certain time, at an instant velocity of both the blocks will be same and let it be and take that extension of spring is . As the floor is smooth we can use law of conservation of energy.
After a certain time, at an instant velocity of both the blocks will be same and let it be and take that extension of spring is . As the floor is smooth we can use law of conservation of energy.
Definition
Frame of reference
Inertial frame of reference are frames of reference which have zero acceleration. Force on a body in an inertial frame of reference due to the reference frame is zero.
Non-Inertial frame of reference are frames of reference which have non-zero acceleration. Force on a body in an inertial frame of reference due to the reference frame is non-zero and opposite to the direction of acceleration of the frame of reference.
Non-Inertial frame of reference are frames of reference which have non-zero acceleration. Force on a body in an inertial frame of reference due to the reference frame is non-zero and opposite to the direction of acceleration of the frame of reference.
Definition
Pseudo Force
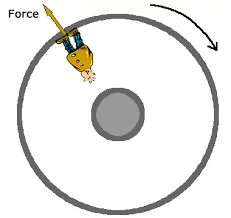
Pseudo Force also called as the fictitious Force, Inertial Force or d'Alembert Force is an apparent Force that acts on all masses whose Motion is described using a Non-Inertial frame of reference that is undergoing Acceleration with respect to an Inertial frame. (e.g. Rotating reference frame).
The direction of the Pseudo Force is always opposite to the direction of the acceleration of frame of reference. This force always acts on the body in motion which is under consideration. Since it is also a force, it depends on two parameters, the mass, and the acceleration.
The direction of the Pseudo Force is always opposite to the direction of the acceleration of frame of reference. This force always acts on the body in motion which is under consideration. Since it is also a force, it depends on two parameters, the mass, and the acceleration.
Definition
Apparent weight of a man in a Lift/ Elevator

Suppose a person having mass is standing on a weighing machine which is placed in a stationary lift.
In this case, the actual weight of a person is
This acts on that weighing machine which offers a normal reaction N, which is nothing but the reading of weighing machine.
This reaction exerted by on the man is the apparent weight of the man.
But this apparent weight will depend upon the motion of lift.
Let us see how it depends upon the motion of lift.
1. When the lift will be at rest or moving with a uniform velocity no matter upwards or downwards, the apparent weight, i.e., actual weight of a man.
From FBD,
2. When the lift will be accelerating upwards with an acceleration .From FBD we can see that
In this case, the apparent weight of the man has become more than the actual weight.
3. When the lift will be accelerating downwards with an acceleration a. From FBD,
In this case, the apparent weight of the man has become less than the actual weight.
Note : If at any moment of time, cable of lift get broke down, then the reading of weighing machine will be 0.
Because both man and lift will be freely falling in this case. This phenomenon is known as "weightlessness".
In this case, the actual weight of a person is
This acts on that weighing machine which offers a normal reaction N, which is nothing but the reading of weighing machine.
This reaction exerted by on the man is the apparent weight of the man.
But this apparent weight will depend upon the motion of lift.
Let us see how it depends upon the motion of lift.
1. When the lift will be at rest or moving with a uniform velocity no matter upwards or downwards, the apparent weight, i.e., actual weight of a man.
From FBD,
2. When the lift will be accelerating upwards with an acceleration .From FBD we can see that
In this case, the apparent weight of the man has become more than the actual weight.
3. When the lift will be accelerating downwards with an acceleration a. From FBD,
In this case, the apparent weight of the man has become less than the actual weight.
Note : If at any moment of time, cable of lift get broke down, then the reading of weighing machine will be 0.
Because both man and lift will be freely falling in this case. This phenomenon is known as "weightlessness".
Definition
Definition of a System

A set of things working together as parts of a mechanism or an interconnecting network. In order to study motion for a particular set of objects system is defined and different physical quantities like momentum, energy etc are calculated.
Example
Total contact force between surfaces

Example: For the arrangements shown in figure, acceleration of block B is upwards. Find the normal reaction (in ) between the
surfaces of contact of the two blocks.
Solution: Let horizontal direction is and vertical direction is and is normal force between inclined surfaces, perpendicular to surface
direction,then constrained motion is defined as
then
surfaces of contact of the two blocks.
Solution: Let horizontal direction is and vertical direction is and is normal force between inclined surfaces, perpendicular to surface
direction,then constrained motion is defined as
then
Example
Calculate acceleration and force on blocks kept in contact

Problem:
Two blocks are kept in contact with each other on a smooth surface. The force on the lighter block and its acceleration is:
Solution: Given : N kg kg
Total mass of the system kg
Net acceleration of the system
Thus acceleration of lighter block is
Also force acting on the lighter block
Two blocks are kept in contact with each other on a smooth surface. The force on the lighter block and its acceleration is:
Solution: Given : N kg kg
Total mass of the system kg
Net acceleration of the system
Thus acceleration of lighter block is
Also force acting on the lighter block
Example
Readings of Weighing Machines

Two masses which are connected with a light string, are placed over a frictionless pulley. This set up is placed over a weighing machine, as shown. Three combination of masses are used, in first case 6 kg and 2 kg, in second case 5 kg and 3kg and in third case 4 kg and 4 kg. Masses are held stationary initially and then released. If the readings of the weighing machine after the release in three cases are
respectively then : Reading of the weighing machine 2T + weight of the machine. As weight of the machine is constant.
So reading is maximum for the case is maximum as in all cases is same.
respectively then : Reading of the weighing machine 2T + weight of the machine. As weight of the machine is constant.
So reading is maximum for the case is maximum as in all cases is same.
Example
Motion of Objects with respect to frames accelerated in one dimension
For example, the magnitude of the pseudo force on a driver by the racing car he operates (mass of the driver is 80 kg), as it accelerates horizontally along a straight line from rest to m/s in s would be estimated by this:
There are two ways to solve this problem :
1. Using equations of motion to calculate acceleration and subsequently force :
initial velocity u
final velocity v
time t s
Using the equation of motion, (where a is the acceleration)
We get
Force mass times acceleration
2. Using the Newton's second law of motion,
Initial momentum
Final momentum
Force
There are two ways to solve this problem :
1. Using equations of motion to calculate acceleration and subsequently force :
initial velocity u
final velocity v
time t s
Using the equation of motion, (where a is the acceleration)
We get
Force mass times acceleration
2. Using the Newton's second law of motion,
Initial momentum
Final momentum
Force
| BookMarks |
0 Comments
Post a Comment