Definition
Derivation of newton's second law of motion
From newton's second law of motion,
For simplicity, the constant of proportionality is chosen to be .
For simplicity, the constant of proportionality is chosen to be .
Definition
Qualitative meaning of force
Force is a quantity which changes the velocity of a body. So, a body that is sliding stops because frictional force opposes relative motion.
Definition
Applications of second law of motion
According to Newton's second law:
If time interval for the application of force is increased then the value of applied force will decrease. Cricketers use this while catching the ball. They pull their hands backwards so that time of contact with ball increase and less jerk they would experience due to motion of ball.
If time interval for the application of force is increased then the value of applied force will decrease. Cricketers use this while catching the ball. They pull their hands backwards so that time of contact with ball increase and less jerk they would experience due to motion of ball.
Definition
Second Law of Motion
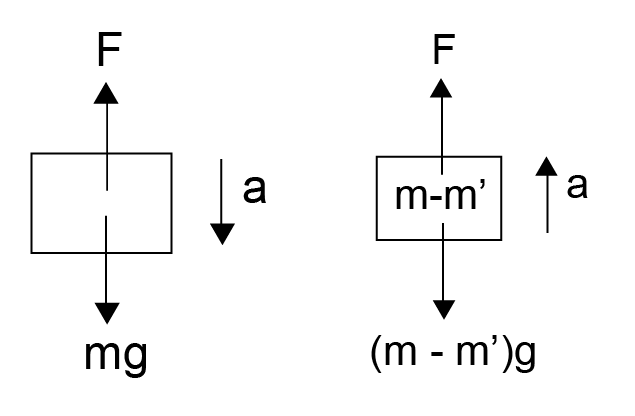
A balloon with mass 'm' is descending down with an acceleration 'a' (where a< g). The mass that should be removed from it so that is starts moving up with an acceleration 'a' will be given by:
.... (1)
from (1)
.... (1)
from (1)
Law
Third Law of Motion
To every action, there is always equal and opposite reaction, i.e.
.
.
Definition
Applications of third law of motion
Newton's third law states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. As you stand on the ground, your body push on the earth with a force, and the earth reacts on your body with the same force in opposite direction. This is an example of Newton's third law.
Result
Newton's Third Law from Law of Conservation of Momentum
Consider an isolated system consisting of two particles.
= Momentum of the whole system, and
and are the respective momentum of the particles.
On differentiating both sides with respect to time, we wiil get
But from Newton Second's Law, we know that
But we know that the momentum remains conserved in an isolated system,
or
which is Newton's third law.
= Momentum of the whole system, and
and are the respective momentum of the particles.
On differentiating both sides with respect to time, we wiil get
But from Newton Second's Law, we know that
But we know that the momentum remains conserved in an isolated system,
or
which is Newton's third law.
Example
Newton's Law of motion to system of masses

Example: Two blocks A and B of mass and are connected together by a light spring of stiffness . The system is lying on a smooth horizontal surface with the block in contact with a fixed vertical wall as shown in the figure. The block is pressed towards the wall by a distance and then released. There is no friction anywhere. If spring takes time to acquire its natural length then what is the average force on the block by the wall.
Solution:Let is the velocity of mass in natural length of spring, then from conservation of energy we have,
Velocity of centre of mass at this instant,
Now, impulse on system change in momentum of system
Solution:Let is the velocity of mass in natural length of spring, then from conservation of energy we have,
Velocity of centre of mass at this instant,
Now, impulse on system change in momentum of system
Example
Motion of object under constant force
A constant force () is applied on a stationary particle of mass . The velocity attained by the particle in a certain displacement will be proportional to:
We know,
Moreover,
We know,
Moreover,
Definition
Vector Condition for equilibrium
If forces are acting on a particle then at equilibrium:
| BookMarks |
0 Comments
Post a Comment