Definition
Explain spontaneous and stimulated emission
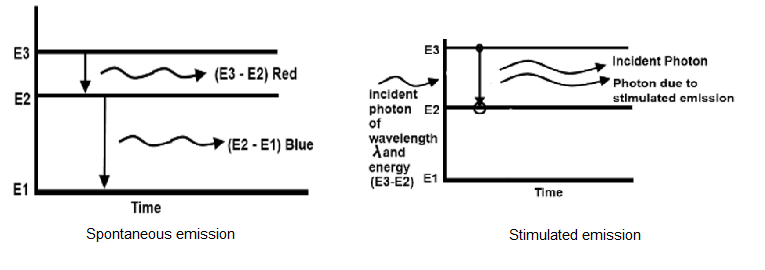
If an atom is in an excited state, it may spontaneously decay into a lower energy level after some time, releasing energy in the form of a photon, which is emitted in a random direction. This process is called spontaneous emission.The simulated emission occurs when a poton with the correct wavelength approaches to an excited atom. If the excited atom has the energy structure such that an electron can drop to the lower level and release an amount of energy equal to the energy or wavelength of incident photon then photon will be emitted from the excited atom. This photon is identical in all respects to the incident photon. The diagram shown for both spontaneous and stimulated emission.
Definition
Threshold frequency
We know that a minimum energy is required for a metal to emit electrons. This energy is called work function of the metal. This energy come from the energy of light. Hence we can also say that the light should possess enough energy for the electrons to emit. The energy of light depends on frequency. More the frequency more will the energy of light. Hence we may also say that there is a minimum frequency of the light required for the electrons to emmit. This frequency is called threshold frequency.
Definition
Describe a vacuum tube

A vacuum tube is an arrangement of evacuated glass bulb, with electrodes fitted inside. They are much bigger than the diode and the transistor and consume higher power.
Definition
Description of MASER and its application.

MASER stands for Microwave Amplification by Stimulation Emission of Radiation. A LASER is a MASER that works with higher frequency photons in the ultraviolet or visible light spectrum (photons are bundles of electromagnetic energy commonly thought of as "rays of light" which travel in oscillating waves of various wavelengths) .
In each frame, a molecule in the upper level of the MASER transition (that is, in the high energy, excited state) is indicated by a large red circle, while one in the lower level (low energy state) is indicated by a small blue circle.
(a) All of the molecules are in the upper state and a photon of wavelength l (shown in green) is incident from the left.
(b) The photon l stimulates emission from the first molecule, so there are now two photons of wavelength l, in phase.
(c) These photons stimulate emission from the next two molecules, resulting in four photons of wavelength l.
(d) The process continues with another doubling of the number of photons.
The following are the uses of MASER
1. MASER is used in satellite communication.
2. It is also used in air to air communication.
3. We use MASER in radio telescope.
4. MASER is also used in radar technology
In each frame, a molecule in the upper level of the MASER transition (that is, in the high energy, excited state) is indicated by a large red circle, while one in the lower level (low energy state) is indicated by a small blue circle.
(a) All of the molecules are in the upper state and a photon of wavelength l (shown in green) is incident from the left.
(b) The photon l stimulates emission from the first molecule, so there are now two photons of wavelength l, in phase.
(c) These photons stimulate emission from the next two molecules, resulting in four photons of wavelength l.
(d) The process continues with another doubling of the number of photons.
The following are the uses of MASER
1. MASER is used in satellite communication.
2. It is also used in air to air communication.
3. We use MASER in radio telescope.
4. MASER is also used in radar technology
Definition
Hertz experiment in production of electromagnetic waves

To test Maxwell's hypothesis, Hertz used an oscillator made of polished brass knobs, each connected to an induction coil and separated by a tiny gap over which sparks could leap. To confirm this, Hertz made a simple receiver of looped wire,its ends separated by a tiny gap. The receiver was placed several yards from the oscillator. Hertz reasoned that, if Maxwell's predictions were correct, electromagnetic waves would be transmitted during each series of sparks,that would induce a current in the loop that would send sparks across the gap. This occurred when Hertz turned on the oscillator, producing the first transmission and reception of electromagnetic waves. Hertz also noted that electrical conductors reflect the waves and that they can be focused by concave reflectors. He found that nonconductors allow most of the waves to pass through.
Definition
Experimental study of photoelectric effect
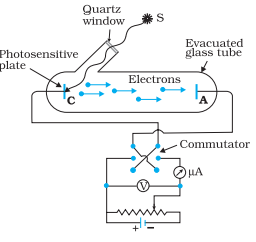
Let us study an experimental setup as shown in the figure. Here a photosensitive C plate is irradiated with light of particular frequency. The plate A is maintained at some potential difference with plate C. Let us study the effects of different factors such as: 1) intensity of light 2) frequency of light 3) potential difference between the plates
Definition
Effect of potential on photoelectric current

- More the potential difference between the plate C and A is increased, the phoelectric current will also increase.
- At some stage, all the photoelectrons ejected by the metal will be accumulated by the collector plate and a saturation in current occurs. This current is called saturation current. After this stage the photocurrent does not increase no matter how much intensity of light is used.
- If we increase the intensity of the light the saturation current also increases.Let initial intensity be and now it is increased to .Hence the saturation current of light with intensity is more than that of
- We now apply a negative (retarding) potential to the plate A with respect to the plate C and make it increasingly negative gradually. When the polarity is reversed, the electrons are repelled and only the most energetic electrons are able to reach the collector A. The photocurrent is found to decrease rapidly until it drops to zero at a certain sharply defined, critical value of the negative potential on the plate A. For a particular frequency of incident radiation, the minimum negative (retarding) potential given to the plate A for which the photocurrent stops or becomes zero is called the cut-off or stopping potential.
Definition
Effect of intensity of light on photocurrent
let us say that the plate A is given a positive potential with respect to the plate C. When the light is incident on the plate C, electrons will be attracted to plate A. More the intensity of the light, more will be the electrons ejected and more will be the photocurrent.
| BookMarks |
0 Comments
Post a Comment