Example
Finding coefficient of friction
Example. A car begins to move at time and then accelerates along a straight track with a speed given by for . After the end of acceleration, the car continues to move at constant speed. A small block initially at rest on the floor of the car begins to slip at . and stops slipping at . Find the coefficient of static and kinetic friction between the block and the floor.
Solution:
At ,
When the block is just starting to slip we have,
Now, it goes on slipping till 3 seconds, therefore in 2 seconds the block's
velocity changes from
Hence, acceleration from to secs is:
Applying equation of motion
Solution:
At ,
When the block is just starting to slip we have,
Now, it goes on slipping till 3 seconds, therefore in 2 seconds the block's
velocity changes from
Hence, acceleration from to secs is:
Applying equation of motion
Definition
Self-adjusting nature of friction
When a moving body is suddenly stopped, then frictional force arises when there is a relative motion between two surfaces. When body is stopped means there is no relative motion and no resultant force is there hence frictional force acting becomes zero.
Definition
Limiting Friction
The maximum static friction that a body can exert on the other body in contact with it is called limiting friction. This limiting friction is proportional to the normal contact force between the two bodies, It is given by:
Diagram
Graph of total external force Vs frictional force

Definition
Angle of Friction
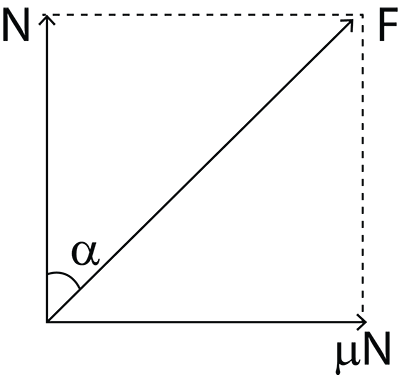
It is the angle ( ), measured between the normal force (N) and resultant force (R).
A body rests on a rough horizontal plane. A force is applied to the body directed towards the plane at an angle with the vertical.
The body can be moved along the plane:
Consider a block placed on a rough horizontal plane. Now, the reaction force is because it is equal and opposite to the
weight . If the force is applied to the block towards the plane at an angle , the resolved forces will act along vertical and horizontal direction.
The horizontal component of force have to overcome the frictional force so that the block just begins to slide. Frictional force is equal to limiting friction , when this condition is satisfied the angle of applied force will be greater than angle of friction and block can move along the plane.
A body rests on a rough horizontal plane. A force is applied to the body directed towards the plane at an angle with the vertical.
The body can be moved along the plane:
Consider a block placed on a rough horizontal plane. Now, the reaction force is because it is equal and opposite to the
weight . If the force is applied to the block towards the plane at an angle , the resolved forces will act along vertical and horizontal direction.
The horizontal component of force have to overcome the frictional force so that the block just begins to slide. Frictional force is equal to limiting friction , when this condition is satisfied the angle of applied force will be greater than angle of friction and block can move along the plane.
Example
Laws of friction and example

Laws of Friction are:
Equating forces along X and Y axes,
Also,
- When an object is moving, the friction is proportional and perpendicular to the normal force (N)
- Friction is independent of the area of contact as long as there is an area of contact.
- The coefficient of static friction is slightly greater than the coefficient of kinetic friction.
- Within rather large limits, kinetic friction is independent of velocity.
- Friction depends upon the nature of the surfaces in contact.
Equating forces along X and Y axes,
Also,
Example
Kinetic Friction: Explained
Frictional force that opposes relative motion between surfaces in contact is called kinetic or sliding friction and is denoted by . It is given by:
where is the coefficient of kinetic friction, which depends only on the surfaces in contact and is the normal force.
Example: When a wooden block is sliding on the floor the friction acting between the wood surface and the floor will be kinetic friction.
where is the coefficient of kinetic friction, which depends only on the surfaces in contact and is the normal force.
Example: When a wooden block is sliding on the floor the friction acting between the wood surface and the floor will be kinetic friction.
Formula
relation between normal reaction and friction force

When two bodies are kept in contact, electromagnetic forces act between the charged particles at the surfaces of the bodies. Thus, each body exerts a contact force of the other. The magnitudes of the contact forces acting on the two bodies are equal but their directions are opposite and therefore the contact forces obey Newton's third law.
The direction of the contact forces acting on a body is not necessarily perpendicular to the contact surface. The resolution of contact forces in two components i.e. perpendicular to contact surface and along surface.
Perpendicular component is normal force and parallel component is friction.
R =
R - Contact force
The direction of the contact forces acting on a body is not necessarily perpendicular to the contact surface. The resolution of contact forces in two components i.e. perpendicular to contact surface and along surface.
Perpendicular component is normal force and parallel component is friction.
R =
R - Contact force
Definition
Normal Reaction
When any two surfaces are in contact, a contact force is exerted between the surfaces. Normal reaction is the component of the contact force normal to the contact surface.
For example, for a block placed on ground, the ground exerts an upward normal reaction force on the block.
For example, for a block placed on ground, the ground exerts an upward normal reaction force on the block.
Example
Normal reaction forces in real life
Some examples of normal reaction forces in real life are:
1. When standing on the ground, we feel a normal reaction equal to the weight due to the ground. This principle is used to measure the weight of a body.
2. A boy pushing a wall feels a normal reaction force due to the wall equal to the force applied on the wall.
1. When standing on the ground, we feel a normal reaction equal to the weight due to the ground. This principle is used to measure the weight of a body.
2. A boy pushing a wall feels a normal reaction force due to the wall equal to the force applied on the wall.
| BookMarks |
0 Comments
Post a Comment