Definition
Electric potential
Electric potential () at a point is defined as the amount of work done in bringing a unit positive charge from infinity to that point.
Unit of potential is .
Note: Potential is taken to be zero at infinity and at ground.
Unit of potential is .
Note: Potential is taken to be zero at infinity and at ground.
Definition
Electric potential energy
Electric potential energy of charge q at a point (in the presence of field due to any charge configuration) is the work done by the external force (equal and opposite to the electric force) in bringing the charge q from infinity to that point.
Definition
Potential difference
Potential difference between two points is the work done in moving a unit positive charge between the two points. Its unit is (Volts).
Definition
Potential due to a continuous charge
where is the charge of an element of the continuous distribution.
Result
Work done by a given charge
Work done by a charge to move through a potential difference is given by .
Where = Final potential and = Initial potential
Where = Final potential and = Initial potential
Definition
Energy density of a medium
Energy density is the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume or mass.
Energy density in an isotropic medium:
Energy density in an isotropic medium:
Formula
Electric potential due to a point charge

where is a point charge and is the potential due it at a point of r distance.
Example
Potential due to a system of charges

An infinite number of charges each equal to 'q' are placed along the X-axis at , , , ..... The potential at the point x = 0 due to this set of charges is
We know V due to charge q
V is a scalar quantity
total potential at 0 is just sum of all charges.
(sum of infinite
V is a scalar quantity
total potential at 0 is just sum of all charges.
(sum of infinite
Formula
Potential due to an infinitely long uniformly charged wire

where is the length of the wire, and is the perpendicular distance from the wire where the potential is calculated
Formula
Potential due to a infinitely charged sheet
where , is the surface charge density and is the distance from the plate.
Formula
Potential due to a uniformly charged ring
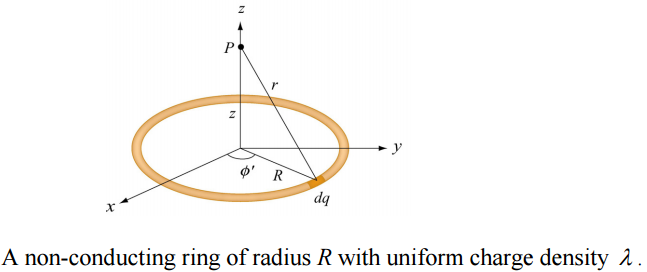
Potential due to uniformly charged ring on its axis:
Formula
Potential due to a uniformly charged disc

where is the surface charge density
| BookMarks |
Page 11 Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15
0 Comments
Post a Comment