Definition
Differences between self and mutual inductance
| Self-induction | Mutual induction | |
| 1. | When the current flows in coil changes, an induced current is produced in the same coil. This is called Self induction | When 2 coils are placed near each other and current is changing in one coil, an induced current is produced in another coil. This is called Mutual induction |
| 2. | Here one coil is used | Here 2 coils are used |
| 3. | Induced current affects the main current | The induced current is produced in the second coil, therefore main current is not affected. |
Definition
Mutual inductance between 2 plane circular coils
Consider 2 plane circular coils close to each other having same axis. The radius of first coil is and turns and secondary coil be and turns be .
When current I flows through primary coil then magnetic field at centre be
Due to magnetic field the flux linked with secondary coil be
but
When current I flows through primary coil then magnetic field at centre be
Due to magnetic field the flux linked with secondary coil be
but
Example
Mutual inductance of two long co-axial solenoids
A straight solenoid of length m has turns in the primary and turns in the secondary. If the area of cross section is , the mutual inductance will be:
Definition
Self inductance
Self inductance is defined as the induction of a voltage in a current-carrying wire when the current in the wire itself is changing. In the case of self-inductance, the magnetic field created by a changing current in the circuit itself induces a voltage in the same circuit. Therefore, the voltage is self-induced.The self-inductance of the coil depends on its geometry and on the permeability of the medium.
Definition
Experimental demonstration of Self Inductance
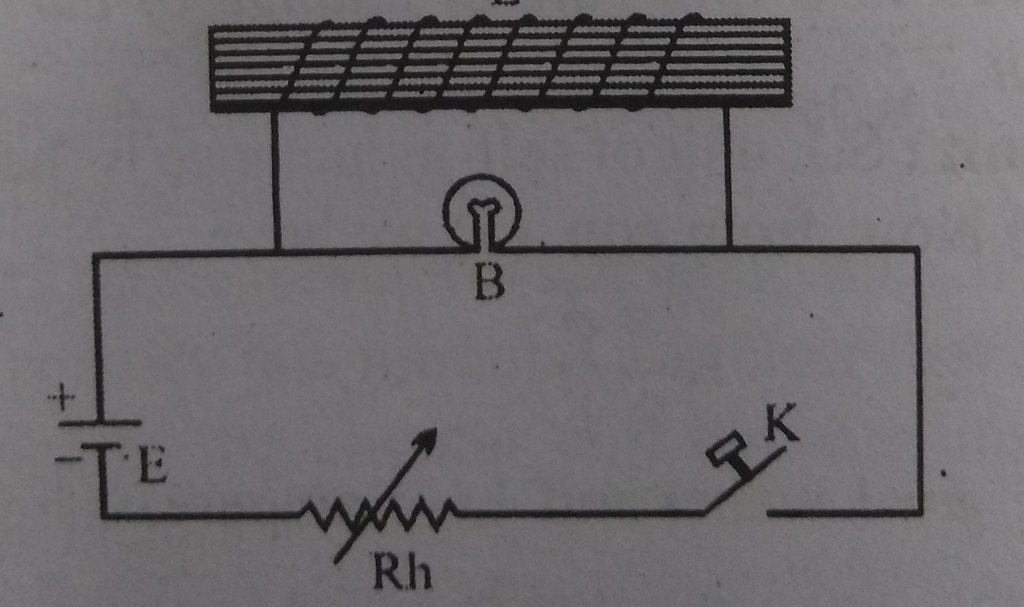
The circuit of experiment is shown in fig.,
L is insulated copper coil wound on soft iron core. Cell E, rheostat Rh and key K is connected in series to coil. A bulb is connected in parallel
When Key K is closed, the bulb glows and then becomes bright and when key K is open the bulb flashes brightly and then goes out. This is because of self induction
Reason:When key is opened the flux linked with coil decreases to zero. Thus, induced current flows in the direction of main current causes increase in the intensity of current momentarily and hence the bulb flashes brightly, and then it goes out.
It is for this reason that of switch is suddenly made off, then bulb gets fused.
L is insulated copper coil wound on soft iron core. Cell E, rheostat Rh and key K is connected in series to coil. A bulb is connected in parallel
When Key K is closed, the bulb glows and then becomes bright and when key K is open the bulb flashes brightly and then goes out. This is because of self induction
Reason:When key is opened the flux linked with coil decreases to zero. Thus, induced current flows in the direction of main current causes increase in the intensity of current momentarily and hence the bulb flashes brightly, and then it goes out.
It is for this reason that of switch is suddenly made off, then bulb gets fused.
Definition
Back emf
The back electromotive force, is the voltage, or electromotive force, that pushes against the current which induces it. Back emf is the voltage drop in an alternating current (AC) circuit caused by magnetic induction.For example, the voltage drop across an inductor is due to the induced magnetic field inside the coil.The voltage's polarity is at every moment the reverse of the input voltage.
Definition
Voltage drop in internal resistance of a cell

Voltage drop in internal resistance of a cell is given by:
where
Current drawn from the cell
Internal resistance of the cell
In the attached figure, its value is
where
Current drawn from the cell
Internal resistance of the cell
In the attached figure, its value is
Definition
Back emf playing the role of inertia
The self-induced emf is also called the back emf as it opposes any change in the current in a circuit. Physically, the self-inductance plays the role of inertia. It is the electromagnetic analogue of mass in mechanics.So, work needs to be done against the back emf in establishing the current. This work done is stored as magnetic potential energy.
| BookMarks |
0 Comments
Post a Comment