Definition
Instantaneous power in an LCR circuit
The instantaneous power supplied by the source is
Formula
Average power in an LCR circuit
The average power over a cycle in an LCR circuit is given as
Definition
Resonance in LC circuit
Resonance occurs when an LC circuit is driven from an external source at an angular frequency at which the inductive and capacitive reactances are equal in magnitude. The frequency at which this equality holds for the particular circuit is called the resonant frequency. The resonant frequency of the LC circuit is:
where L is the inductance in henries, and C is the capacitance in farads. The angular frequency has units of radians per second.
where L is the inductance in henries, and C is the capacitance in farads. The angular frequency has units of radians per second.
Definition
Sharpness of resonance
The quantity () is regarded as a measure of the sharpness of resonance. The smaller the , the sharper or narrower is the resonance. Here, is the resonant frequency, is the bandwidth.
Definition
Half power points of resonance

For values of other than , the amplitude of the current is less than the maximum value. Suppose we choose a value of for which the current amplitude is times its maximum value. At this value, the power dissipated by the circuit becomes half. There are two of these half-power frequencies, one above, and one below the resonance frequency which are called half power points of resonance.
Definition
Bandwidth of resonance circuits
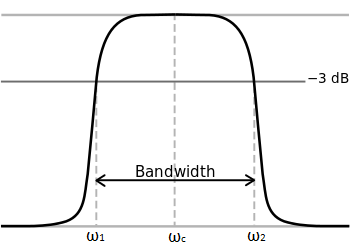
The bandwidth is measured between the 3dB points, that is, the frequencies at which the power passed through the circuit has fallen to half the value passed at resonance. The bandwidth is the difference between the half power frequencies i.e
Bandwidth,
Bandwidth,
Example
Quality factor
The Q factor of a resonance circuit is given as
where is the resonant frequency
Example: The values of and in an series circuit are and respectively. The quality factor of the current is =100
where is the resonant frequency
Example: The values of and in an series circuit are and respectively. The quality factor of the current is =100
Definition
Quality factor and its relevance with selectivity
The Q factor is a widespread measure used to characterize resonators. It is defined as the peak energy stored in the circuit divided by the average energy dissipated in it per radian at resonance. Low Q circuits are therefore damped and lossy and high Q circuits are under-damped. Q is related to bandwidth; low Q circuits are wide band and high Q circuits are narrow band. In fact, it happens that Q is the inverse of fractional bandwidth.
Q factor is directly proportional to selectivity, as Q factor depends inversely on bandwidth.
Q factor is directly proportional to selectivity, as Q factor depends inversely on bandwidth.
Definition
Comparison of power dissipated in various circuits
Power dissipated is given as .
Resistive circuit: If the circuit contains only pure , it is called resistive. In that case 0, . There is maximum power dissipation.
Purely inductive or capacitive circuit: If the circuit contains only an inductor or capacitor, we know that the phase difference between voltage and current is . Therefore, , and no power is dissipated even though a current is flowing in the circuit. This current is sometimes referred to as wattless current.
LCR series circuit: In an LCR series circuit,. So, may be non-zero in a RL or RC or RCL circuit. Even in such cases, power is dissipated only in the resistor.
Power dissipated at resonance in LCR circuit: At resonance . Therefore, and . That is,maximum power is dissipated in a circuit (through R) at resonance.
Resistive circuit: If the circuit contains only pure , it is called resistive. In that case 0, . There is maximum power dissipation.
Purely inductive or capacitive circuit: If the circuit contains only an inductor or capacitor, we know that the phase difference between voltage and current is . Therefore, , and no power is dissipated even though a current is flowing in the circuit. This current is sometimes referred to as wattless current.
LCR series circuit: In an LCR series circuit,. So, may be non-zero in a RL or RC or RCL circuit. Even in such cases, power is dissipated only in the resistor.
Power dissipated at resonance in LCR circuit: At resonance . Therefore, and . That is,maximum power is dissipated in a circuit (through R) at resonance.
Definition
Wattless Current
The current in an AC circuit is said to be Wattless Current when the average power consumed in such circuit corresponds to Zero.Such current is also called as Idle Current.
This mainly happens in a purely inductive or capacitive circuit only.This is because,in both inductive and capacitive circuits,the voltage and current differ by a phase angle of 90. As the average power depends upon the cos component which becomes zero as the angle between them is ninety.
This mainly happens in a purely inductive or capacitive circuit only.This is because,in both inductive and capacitive circuits,the voltage and current differ by a phase angle of 90. As the average power depends upon the cos component which becomes zero as the angle between them is ninety.
Definition
Power factor
The quantity is called the power factor. The power factor of an a.c. circuit having L and R connected in series to an a.c. source of angular frequency is given by
Power factor
Power factor
| BookMarks |
0 Comments
Post a Comment