Definition
Isochoric process
An isochoric process is a thermodynamic process during which the volume of the closed system undergoing such a process remains constant. An isochoric process is exemplified by the heating or the cooling of the contents of a sealed, inelastic container
Definition
Work done in an isochoric process
Here .
Diagram
PV,TV,PT diagrams for an isochoric process

Definition
Reversible process
A thermodynamic process is reversible if the process can be turned back such that both the system and the surroundings return to their original states, with no other change anywhere else in the universe.
Example: two metal jars A and B are at a thermal equilibrium and are in contact with each other. Now when we heat jar A slightly, heat starts to flow from Jar A to Jar B. This is the direction of this process. Now this process can be reversed just by cooling Jar A slightly. When Jar A is cooled, heat flows from Jar B to Jar A till thermal equilibrium is reached.
Example: two metal jars A and B are at a thermal equilibrium and are in contact with each other. Now when we heat jar A slightly, heat starts to flow from Jar A to Jar B. This is the direction of this process. Now this process can be reversed just by cooling Jar A slightly. When Jar A is cooled, heat flows from Jar B to Jar A till thermal equilibrium is reached.
Definition
Irreversible process
A process is said to be irreversible if it cannot return the system and the surroundings to their initial states when the process is reversed. The irreversible process is not at equilibrium throughout the process.For example, free expansion of a fluid
Definition
Isothermal process
An isothermal process is one in which the temperature is constant.
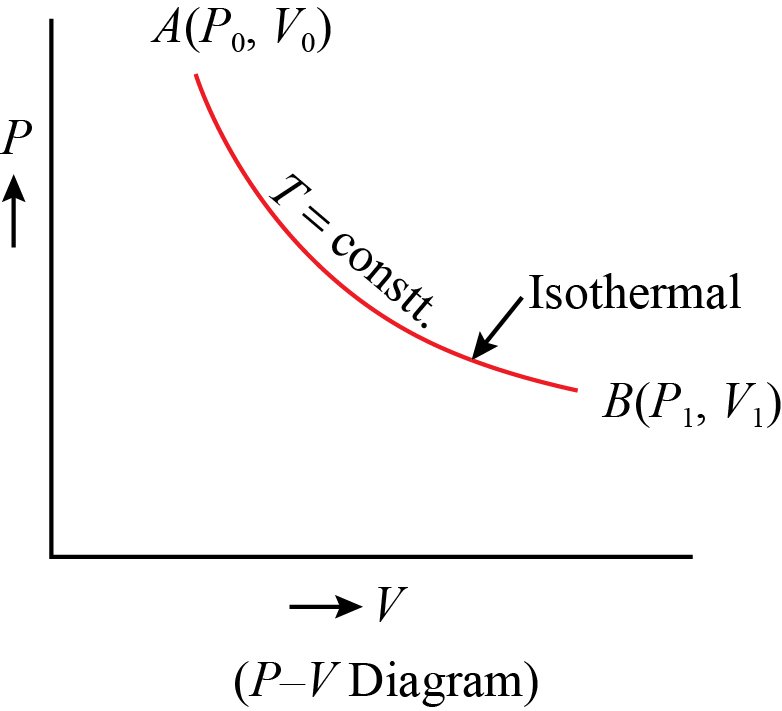
Diagram
PV diagram of an isothermal process
Formula
Work done in an isothermal process
Definition
Adiabatic process
In an adiabatic process, the system is insulated from the surroundings and heat absorbed or released is zero. For an adiabatic process of an ideal gas,
where is the ratio of specific heats (ordinary or molar) at constant pressure and at constant volume.
where is the ratio of specific heats (ordinary or molar) at constant pressure and at constant volume.
Example
P-V relation for an adiabatic process
For an adiabatic process,
On simplification and putting we get
Example :
A polyatomic gas is compressed to of its volume adiabatically. If its initial pressure is P, the new pressure will be:In an adiabatic process we have constant .
or
Therefore if become . Substituting values in the equation will give final P to be .
On simplification and putting we get
Example :
A polyatomic gas is compressed to of its volume adiabatically. If its initial pressure is P, the new pressure will be:In an adiabatic process we have constant .
or
Therefore if become . Substituting values in the equation will give final P to be .
| BookMarks |
Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15
0 Comments
Post a Comment