Formula
Efficiency of a heat engine
where is the heat absorbed from the source,
is the heat released to the sink,
is the work output in one cycle,
is the efficiency
Definition
Limitations of Steam Engine
Limitations of Steam Engine:
- Construction of steam engine is not as simple as shown in the diagram. The fuel chamber is not shown in the diagram. The bulk and the heavy weight of the engine is not suitable for small vehicles.
- The efficiency of the engine is very low. There is more loss of heat in this type of engine. Much of the heat is lost in the boiling of water,to increase the temperature of water to its boiling point.
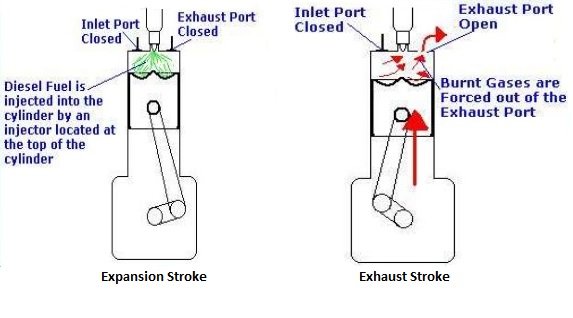
- Heating water, to produce steam, takes time and the engine cannot start instantly. To keep the steam ready, the fuel should be burnt continuously even if the engine is at rest. The limitations of steam engine lead to the discovery of internal combustion engine. Rudolf Diesel and Nikolaus were the two pioneers in this effort. Today internal combustion engines are used in all transport vehicles, Scooters, cars, buses, lorries and trains all work using internal combustion engines. Depending upon the fuel used, internal combustion engines are of two types. They are petrol engine and diesel engine.
Law
Working of a Steam Engine
Working of a Steam Engine:Water is heated in a boiler, to generate steam of high pressure which is passed into a cylinder fitted with a piston. As steam occupies a much larger volume than the same amount of water, it exerts great pressure on the walls of the container in all directions. As the steam expands in the cylinder, it pushes the piston forward. Crankshaft connected to the piston also moves. Crank shaft converts linear movement of the piston into circular motion. The wheel of the crank shaft makes half rotation during the expansion stroke. Steam expands and it pushes the piston forward and loses some of its kinetic energy. As a result, it condenses into water. The piston is then pushed back into the cylinder due to low pressure region. Due to inertia of the crank shaft, the wheel makes another half rotation and completes one cycle.This is exhaust stroke. The condensed water is expelled out and fresh steam is let in to repeat the process. In steam engines, the fuel, mainly coal is burnt outside the engine. In steam engines, there are special shutters called valves. Valves open in one direction only to let in or to let out steam at appropriate stages.
Definition
Limitations of Steam Engine
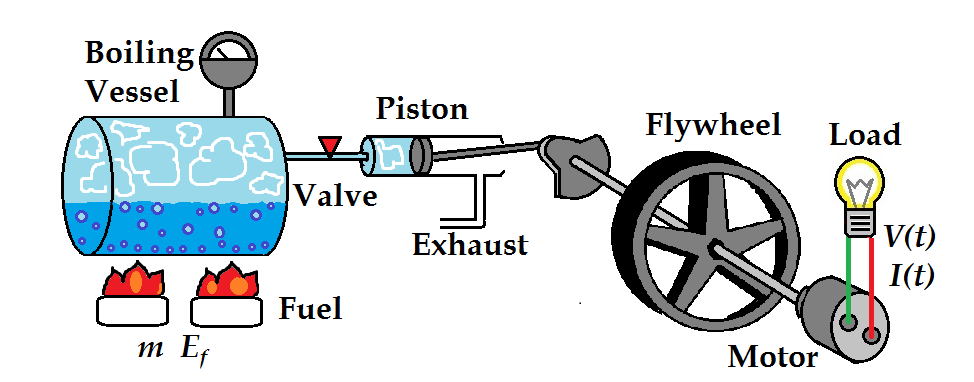
Following are the limitations of steam engine :
- A steam engine is huge and heavy due to which it cannot be used for running small vehicles like cars and buses.
- A steam engine does not start at once. In order to start it, we have to build a coal fire to get steam.
- A steam engine is not very safe to use because its boiler can burst due to excessive steam pressure.
- A steam engine has low efficiency because most of the heat get lost due large surface area of the steam engine.
Definition
Carnot's Theorem
All reversible engines operating between the same two temperatures have equal efficiency and no engine operating between the same two temperature can have an efficiency greater than this.
Definition
Proof of Carnot's theorem

According to the Carnot theorem, the reversible engine (say ) will always have a greater efficiency than the irreversible one ().
We assume that the efficiency of is greater than that of . Accordingly, the work done by , is greater than the work done by . Now, let the reversible heat engine be operated on a reverse cycle so that it functions as a heat pump (or refrigerator). Let the work input to this heat pump be taken from the work output of the irreversible engine (since we have said that is greater than ).If you look at this closely, you will see that the net energy exchange in the reservoir at is zero.
Thus, the net effect of our new device is to convert heat of into an amount of work .
This is a violation of the Kelvin-Planck statement of the second law of thermodynamics, since there is no heat rejected to a sink, making this a perpetual motion machine of the second kind.This means that our initial assumption was false, thus proving elegantly that the Carnot theorem is correct.
Definition
Steps in a Carnot cycle

The Carnot cycle when acting as a heat engine consists of the following steps:
- Reversible isothermal expansion of the gas at the "hot" temperature, T1 (isothermal heat addition or absorption).
- Isentropic (reversible adiabatic) expansion of the gas (isentropic work output)
- Reversible isothermal compression of the gas at the "cold" temperature, T2. (isothermal heat rejection)
- Isentropic compression of the gas (isentropic work input).
| BookMarks |
Page 12 Page 13 Page 14 Page 15
0 Comments
Post a Comment